Healthcare accounting has developed far beyond spreadsheets and manual billing. In today’s complex medical landscape, hospitals and healthcare organizations across the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia rely on precise financial tracking to stay compliant, profitable, and patient-focused. Rising costs, strict data privacy laws, and growing demand for digital health services have made financial transparency a necessity—not a choice.
Table of Contents
A single billing error or misclassified expense can trigger compliance audits, impact funding, or reduce trust among stakeholders. This is why healthcare accounting professionals play a crucial role in protecting financial integrity while enabling smoother operations across hospitals, clinics, and research institutions.
Modern healthcare accounting combines financial analytics, compliance management, and real-time reporting. It ensures every dollar, pound, or Australian dollar is tracked correctly from patient billing to government reimbursements. Whether it’s Medicare in the US, NHS Trusts in the UK, or provincial systems in Canada, accurate accounting has a direct impact on care quality and organisational sustainability.
In Tier One markets, healthcare accounting is more than just number crunching —it’s the strategic engine driving efficiency, trust, and improved patient outcomes.
What Is Healthcare Accounting and Why Does It Matter for Modern Medical Organizations
Healthcare accounting refers to the systematic process of recording, analysing, and reporting financial transactions in medical organisations. It includes everything from patient billing and insurance claims to budgeting, payroll, and audit compliance.
Unlike general accounting, healthcare accounting addresses complex variables, including insurance reimbursements, government funding, medical inventory costs, and capital expenditures on technology and equipment.
| Key Focus Area | Description |
| Patient Billing | Tracks revenue from treatments, consultations, and services |
| Insurance Reimbursements | Manages claim processing and follow-ups |
| Compliance | Ensures adherence to GAAP, IFRS, and healthcare laws (HIPAA, GDPR) |
| Auditing | Prevents fraud and supports transparent reporting |
| Forecasting | Project’s financial needs for staffing, tech upgrades, and expansion |
Why it matters: A well-structured healthcare accounting system secures financial stability, supports decision-making, and keeps institutions compliant with ever-changing regulations.
Regular audits and digital accounting tools can reduce reporting errors by up to 35%, improving both profitability and compliance readiness.
What Does a Healthcare Accountant Do? Roles, Skills & Industry Value
Healthcare accountants are the financial backbone of medical organisations. Their role expands beyond basic bookkeeping—they translate complex healthcare data into actionable insights for executives and regulators.
Key Responsibilities of Accounting in Healthcare Institutions
- Managing budgets for hospital departments
- Tracking revenue from multiple payer sources (patients, insurers, government)
- Ensuring GAAP or IFRS compliance in financial statements
- Assisting in strategic decisions through financial forecasting
- Conducting audits and preventing fraudulent claims
Core Skills Required
- Strong knowledge of healthcare laws (HIPAA, SOX, NHS Finance Guidelines)
- Mastery of accounting software such as QuickBooks, Xero, or Oracle NetSuite
- Data analysis and reporting skills
- Ethical and detail-oriented approach
In Tier One countries, healthcare accountants play a crucial role in ensuring operational sustainability. With the healthcare industry representing over 10% of GDP in most of these economies, demand for skilled professionals continues to surge.
Result: Healthcare organisations that employ certified accountants experience 25–40% higher accuracy in billing and compliance reporting compared to those using general finance staff.
Why Accurate Accounting Is Critical for Healthcare Providers in Tier One Markets
Accurate accounting guarantees healthcare providers meet both financial and ethical obligations. In nations like the USA and the UK, where funding models combine private insurance and public reimbursement, precision in financial documentation is crucial for maintaining trust and operational continuity.
Errors can result in:
- Lost reimbursements
- Regulatory penalties
- Damaged reputation
- Resource misallocation
| Market | Regulatory Framework | Key Accounting Standards |
| United States | HIPAA, GAAP, CMS Guidelines | FASB Standards |
| United Kingdom | NHS Finance Manual, GDPR | IFRS Standards |
| Canada | Provincial Health Acts | PSAS (Public Sector Accounting Standards) |
| Australia | My Health Record Act | AASB Standards |
Accuracy in healthcare accounting is not just compliance—it’s a strategic defence against financial inefficiency and data risk.
Healthcare Accounting Solutions – How Technology Streamlines Billing, Auditing & Compliance
Technology has transformed healthcare accounting through automation, cloud-based systems, and AI-powered analytics. Tools like Oracle Fusion Cloud, SAP Healthcare, and QuickBooks Enterprise now automate invoice processing, identify revenue leaks, and simplify audit preparation.
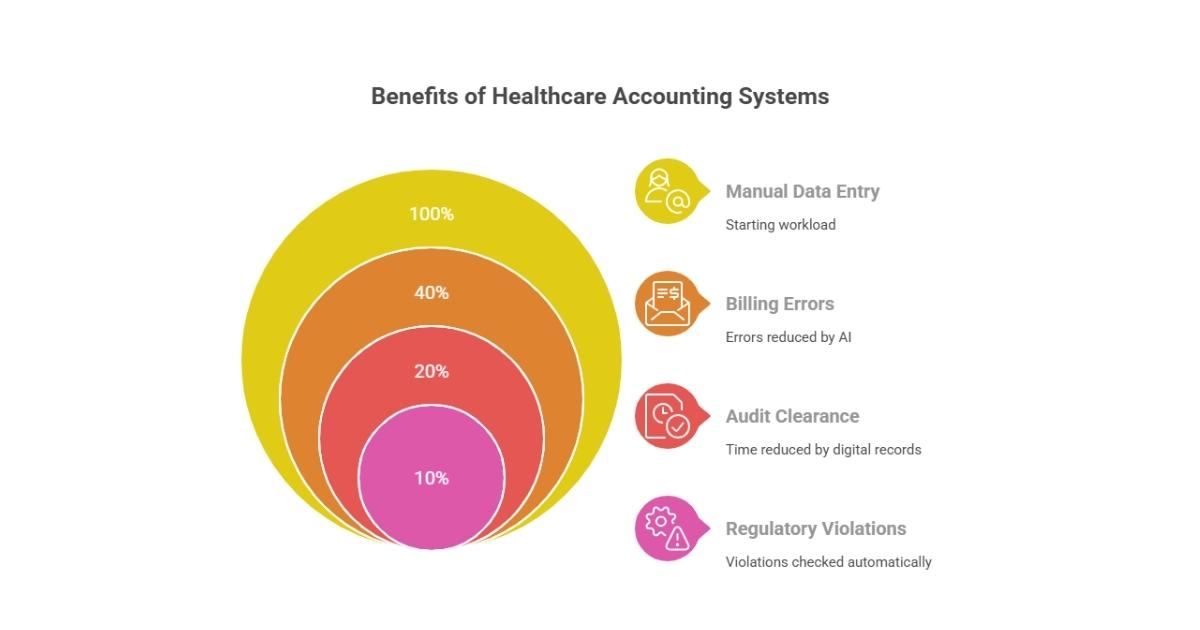
Top Benefits of Implementing Professional Healthcare Accounting Systems
- Reduced Administrative Workload – Automation cuts manual data entry by 50%.
- Improved Accuracy – AI-driven reconciliation reduces billing errors by up to 40%.
- Faster Audits – Digital records speed up audit clearance times.
- Better Compliance – Integrated systems automatically check for regulatory violations.
Result: Hospitals in Australia that adopted cloud accounting reported a 30% decrease in operational costs and significantly faster reimbursement cycles.
Choose solutions with built-in compliance modules that support GAAP, HIPAA, and local data protection laws.
Understanding the Financial Backbone of Healthcare Systems in the US, UK, Canada & Australia
Healthcare systems in Tier One countries differ structurally but share common accounting challenges, including managing high costs, navigating regulations, and ensuring transparency.
- USA: Hospitals balance private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid reimbursements.
- UK: NHS Trusts rely on government budgets and require precise allocation reports.
- Canada: Provinces oversee healthcare funding, demanding detailed financial statements.
- Australia: A hybrid model with both public funding and private practice billing.
| Country | Funding Model | Primary Accounting Challenge |
| USA | Public & Private | Insurance reimbursement accuracy |
| UK | Public (NHS) | Cost control within budgets |
| Canada | Provincial | Inter-departmental transparency |
| Australia | Mixed | Integration of private & public records |
Key Responsibilities of Accounting in Healthcare Institutions
Healthcare accountants are responsible for preparing budgets, analysing revenue streams, monitoring financial transactions, and ensuring regulatory compliance. To improve operations, reduce waste, and prevent financial mismanagement, departments rely on their expertise.
Top Benefits of Implementing Professional Healthcare Accounting Systems
- Enhanced billing accuracy and revenue cycle management
- Streamlined compliance with HIPAA, GAAP, and local standards
- Improved resource allocation across departments
- Better decision-making through real-time analytics
Two Core Types of Accounting in Healthcare: Financial vs. Managerial
- Financial Accounting: External reporting, regulatory compliance, and investor relations.
- Managerial Accounting: Internal budgeting, cost analysis, and operational planning.
How Healthcare Accounting Boosts Profitability, Transparency & Patient Care Quality
Accurate financial oversight supports strategic investment in patient care, reduces waste, and enables cost-effective delivery of healthcare services.
Core Functions of Healthcare Accounting in Hospitals and Medical Networks
Includes accounts payable/receivable, payroll, grant management, budgeting, auditing, and compliance monitoring, all essential to smooth operational functioning.
How Healthcare Accounting Impacts Daily Operations Across Clinical Departments
Every clinical department—from radiology to pharmacy—depends on the reliability of accounting. Cost allocation affects staffing, equipment upgrades, and research budgets.
- Pharmacy accounting: Tracks drug procurement, inventory, and dispensing costs.
- Surgical units: Require real-time reporting on procedure costs and insurance claims.
- Emergency departments: Depend on accurate billing for time-sensitive care.

Efficient accounting systems free up clinicians from administrative burden, improving patient focus and reducing burnout.
Healthcare Accounting vs. General Accounting – Key Differences for Tier One Organizations
| Aspect | General Accounting | Healthcare Accounting |
| Purpose | Profit measurement | Financial efficiency + care outcomes |
| Compliance | GAAP or IFRS | GAAP/IFRS + HIPAA/GDPR |
| Data Sensitivity | Moderate | High (patient-linked data) |
| Reporting | Quarterly/Annual | Continuous + Regulatory |
Healthcare accounting is more managed, data-sensitive, and mission-critical. Always implement role-based access control to safeguard patient-linked financial data.
Essential Financial Reporting for Healthcare Organizations & Compliance Standards
Reporting ensures transparency to both internal and external stakeholders. Healthcare accountants prepare:
- Balance sheets for hospital assets/liabilities
- Income statements for department revenues
- Cash flow statements for operational liquidity
- Compliance reports for regulators and funders
Accurate reporting not only engages investors but also maintains public trust in national health systems.
How to Implement a Healthcare Accounting System That Meets GAAP & HIPAA Compliance
- Assess existing processes – Identify manual bottlenecks.
- Select compliant software – Verify GAAP + HIPAA certifications.
- Train staff – Financial literacy for non-finance teams is key.
- Automate data collection – Link billing, HR, and supply chain systems.
- Regular audits – Use independent auditors for unbiased review.
Organisations that follow this model reduce audit time by 40% and avoid costly noncompliance fines.
Case Study: How Inventory Management Optimization Improved Healthcare Accounting Accuracy (UK Example)
A mid-sized NHS hospital in Manchester launched an automated inventory system integrated with its accounting software. The result?
- Accuracy in medical supply costs increased by 27%.
- Annual savings: £480,000 in reduced wastage and manual errors.
- Audit preparation time: Reduced from 10 days to 4.
This shows how operational transparency directly translates into better financial reporting.
Education, Certification & Training Pathways for Healthcare Accountants (USA & Canada Focus)
To work in healthcare accounting, professionals usually hold:
- Bachelor’s Degree in Accounting, Finance, or Health Administration
- CPA or CMA Certification (USA/Canada)
- Optional: CHFP (Certified Healthcare Financial Professional) or HFMA Membership
Employers prefer accountants with healthcare-specific training; many universities now offer online Healthcare Accounting Diplomas.
Grow Your Career with a Healthcare Accounting Degree or Postgraduate Diploma
Universities in the USA (such as NYU and Johns Hopkins) and Canada (the University of Toronto and McGill) offer specialised degrees focusing on healthcare finance and data analytics.
Outcome: Graduates earn 20–35% higher starting salaries than general accountants.
| Level | Average Annual Salary (USD) |
| Entry-Level | $58,000 – $72,000 |
| Mid-Level | $80,000 – $110,000 |
| Senior / CFO | $130,000 – $200,000+ |
How Cloud Accounting Software Transformed Hospital Finance Management in Australia
A major Australian hospital network adopted cloud accounting integrated with AI.
Results within 12 months:
- Reduced manual invoice processing by 60%.
- Detected duplicate claims early, saving AUD $1.2 million.
- Improved inter-department cost tracking.
Cloud solutions not only improve speed but also enhance compliance with AASB and privacy laws.
Expert Insight – CFO, NHS Trust (UK): “Digitized Accounting Cut Audit Time by 40%”
“Before digitization, audits were chaotic. With automated reporting, our trust reduced audit time by 40%, freeing our finance team to focus on cost improvement and patient care planning.”
— Helen Davies, CFO, NHS South London Trust
Industry Report – Healthcare Finance Trends 2025 (US & Canada)
According to HFMA’s 2025 report:
- 68% of hospitals plan to invest in AI-based accounting systems.
- Data analytics is the top skill in demand for finance teams.
- Over 55% of CFOs say automation is their top cost-control strategy.
Analyst View – How Healthcare Accounting Supports Sustainable Patient Services & Care Models
Financial efficiency leads to better patient outcomes. When hospitals optimise billing and resource allocation, they reinvest savings into new medical equipment, telehealth expansion, and staff training—creating a cycle of continuous care improvement
Statistic Highlight – 68% of Tier One Hospitals Use AI-Enhanced Accounting Tools
AI systems now detect fraud patterns, resolve insurance claims, and forecast cash flow—making financial processes faster and more efficient.
By 2026, expect near-universal adoption of AI-driven accounting in Tier One healthcare systems.
Healthcare Accounting Jobs Outlook: Growing Demand for Data-Driven Finance Professionals
Healthcare accounting jobs are among the fastest-growing finance roles in Tier One countries.
Outlook (2025–2030):
- USA: +8% growth (BLS data)
- UK: +10% demand within NHS Trusts
- Canada: Strong demand for accountants in provincial healthcare
- Australia: +9% growth driven by private sector expansion
Result: Consistent job stability and lucrative pay for certified professionals.
FAQ Section
1. What is accounting in the healthcare industry?
Healthcare accounting manages financial transactions related to medical services, ensuring compliance with regulations specific to the healthcare industry. It covers billing, audits, and funding management for hospitals, clinics, and insurers.
2. What are the 4 types of accountants in healthcare?
The primary types are financial accountants, managerial accountants, auditors, and forensic accountants, each specialising in budgeting, reporting, or fraud prevention.
3. What is GAAP in healthcare accounting?
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are standards that ensure transparent and consistent financial reporting across the healthcare industry, which is crucial for compliance and audits.
4. What is the average healthcare accounting salary in the US, UK, Canada & Australia?
- US: $75,000–$120,000
- UK: £45,000–£80,000
- Canada: CAD $70,000–$110,000
- Australia: AUD $85,000–$130,000
5. Which degree is best for a career in healthcare accounting?
A Bachelor’s degree in Accounting or Finance with a specialisation in healthcare management or compliance is ideal. Postgraduate diplomas in Healthcare Finance add extra value.
6. How does healthcare accounting impact patient care outcomes?
Efficient accounting ensures better resource allocation, reduced financial waste, and reinvestment into patient care infrastructure—leading to improved outcomes.
7. What certifications are required for healthcare accountants?
Key certifications include CPA, CMA, CHFP, and HFMA membership, depending on the region.
8. What are common healthcare accounting jobs and career paths?
Roles include financial analyst, controller, auditor, CFO, and billing specialist within hospitals and healthcare networks.
9. How to get a healthcare accounting course online with accreditation?
Platforms like Coursera, edX, and HFMA offer accredited healthcare accounting courses recognised in Tier One markets.
10. What is included in a healthcare accountant’s job description?
It involves budgeting, preparing financial statements, auditing transactions, managing payroll, and ensuring compliance with laws like HIPAA and GAAP.
<!-- FAQ JSON-LD for: Healthcare Accounting questions (includes concise answers) -->
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is accounting in the healthcare industry?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Healthcare accounting records, classifies and reports financial transactions for healthcare organizations (hospitals, clinics, physician groups). It covers patient billing & collections, payor reimbursements, payroll, cost accounting, grant/fund accounting, financial reporting, and compliance with industry-specific rules to support budgeting and decision-making."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What are the 4 types of accountants in healthcare?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Common roles include (1) Financial/General Accountant (external financial reporting), (2) Management/Cost Accountant (cost analysis, budgeting), (3) Revenue Cycle / Billing & Accounts Receivable Accountant (patient billing, payor reconciliation), and (4) Internal Audit / Compliance Accountant (controls, regulatory compliance)."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is GAAP in healthcare accounting?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) are the U.S. accounting rules and standards (maintained by FASB) that healthcare entities use for preparing financial statements; specific guidance exists for health-care entities (e.g., presentation of patient service revenue, allowances for bad debt) to ensure transparent, consistent reporting."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is the average healthcare accounting salary in the US, UK, Canada & Australia?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Typical mid-level healthcare/accounting roles (approximate, market snapshots as of late 2025): United States ≈ $65,800 per year; United Kingdom ≈ £41,000 per year (medical/medical-accountant average); Canada ≈ CAD $65,000–$68,000 per year (varies by province; Ontario ~CAD $68,300); Australia ≈ AUD $90,000–151,000 per year depending on source and seniority. (Figures are market estimates and vary by experience, city, employer and job title.)"
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Which degree is best for a career in healthcare accounting?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "A bachelor’s degree in accounting or finance is the typical foundation; degrees in healthcare administration with accounting minors are also valuable. For advancement, professional qualifications (CPA, ACCA, CMA) or a master’s (MAcc, MBA with healthcare focus) strengthen prospects."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "How does healthcare accounting impact patient care outcomes?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Accurate accounting supports informed financial decisions (resource allocation, staffing, equipment purchases), efficient revenue cycle operations (so providers remain financially viable), and compliance — all of which enable better access to services, investment in quality improvements, and indirectly improve patient care outcomes."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What certifications are required for healthcare accountants?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Certifica